September 2024
North America News
Canada has issued a notice specific to certain Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS). Pursuant to paragraph 71(1)(b) of the Canadian Environmental Protection Act, 1999 (the Act), for the purpose of assessing toxicity or control methods for described substances, related persons are required to provide specific information no later than 29 January 2025.
The main contents are:
1. Who is required to respond?
This notice applies to any person who, during the 2023 calendar year,
Manufactured a total quantity greater than 1 000 g of any substance listed in Schedule 1.
Imported a total quantity greater than 10 g of a substance listed in Part 1 of Schedule 1, OR a total quantity greater than 100 kg of a substance listed in Part 2 or Part 3 of Schedule 1.
Imported a total quantity greater than 100 kg of any substance listed in Schedule 1 at a concentration ≥ 1 ppm in a manufactured item NOT listed in the categories of manufactured items.
Used a total quantity greater than 10 g of any substance listed in Schedule 1, whether the substance was alone or at a concentration ≥ 1 ppm in a mixture or in a product, in the manufacture of a mixture, a product or a manufactured item.
2. How to determine if you meet the reporting criteria (notice section 2)
Tiered reporting (notice section 3)
If your manufactured item is captured by one of the categories and thresholds are exceeded, you must provide all information that is requested by the notice.
If your manufactured item does not fall into one of the categories and thresholds are exceeded, you will only be required to provide your company information as per notice section 8, and a short description and generic name of the manufactured item containing the substance as per notice section 9.
Successors or assigns (notice section 4)
If a company is sold during the 2023 calendar year, a single response that amalgamates the information before and after the transfer may be submitted for the entire year.
Exclusions (notice sections 5 and 6)
The notice excludes:
Micro-businesses that have fewer than 5 employees or make less than $30,000 in annual gross revenue annually
The notice also excludes substances, mixtures, products and manufactured items that are:
Only in transit through Canada or personal use
Intended for use in a laboratory for analysis, in scientific research
Classified as a hazardous waste or hazardous recyclable material and import / export is in compliance with the Cross-border Movement of Hazardous Waste and Hazardous Recyclable Material Regulations.
Registered under the Pest Control Products Act, Fertilizers Act, Feeds Act or Seeds Act.
3. What information is required (notice sections 7 to 14)
1. If you determine that you meet the reporting criteria of the notice, you must provide a response containing the required information, a summary of which is below:
Identification information (company / organization and person reporting)
Facility information
Quantity of the substance manufactured, imported, used in the manufacture of a good and exported
Information on goods
2. Detailed explanations, examples, and tips for completing your responses to notice sections 8-14 are provided in Annex A.
3. It is important to note that if you own more than one facility, you must consider the reporting criteria on a company-wide basis. Your response to the notice must amalgamate the information from all facilities owned by the company (notice section 7).
Additional information required: Reasonably accessible information; Confidential business information.
4.How to respond to the notice
Once you have determined whether you meet the reporting criteria, there are three ways to respond to the notice:
CEPA section 71 response
If you meet the reporting criteria, you must respond to the notice by submitting the required information in an Excel Reporting File (ERF) to the Government of Canada.
Download the PFAS ERF from the Responding to the PFAS notice webpage.
Complete the required information (instructions are included in Annex A)
Submit the ERF to the Government via Environment and Climate Change Canada’s Single Window (instructions are included in Annex B)
Declaration of Stakeholder Interest (SHI)
If you do not meet the reporting requirements, but have interest in a reportable substance, you can submit a SHI.
The following are partial lists of PFAS that may extend beyond the PFAS listed in the notice:
the OECD Comprehensive Global Database of PFASs (Fluorinated Chemical (oecd.org)),
the US EPA PFASSTRUCT (Chemicals Dashboard (epa.gov)), and the US EPA PRASDEV (Chemicals Dashboard (epa.gov))( instructions are included in Annex B).
Declaration of Non-Engagement (DNE)
If you do not meet the reporting requirements and have no interest in any of the substances, you are encouraged to submit a DNE by emailing substances@ec.gc.ca. Indicate “PFAS DNE” in the subject line of the email and specify your company name and its contact information.
Note: Related persons are required to provide specific information no later than 29 January 2025. As outlined in the guidance manual, failure to respond could result in environmental enforcement action and potential penalties to individuals and corporations.
In the US, when hazards are identified in consumer products, they will be recalled and published in the Consumer Product Safety Commission (CPSC) Recent Recalls on the CPSC website, which is updated daily. The US recalls from 01 August 2024 to 31 August 2024 are summarized below:
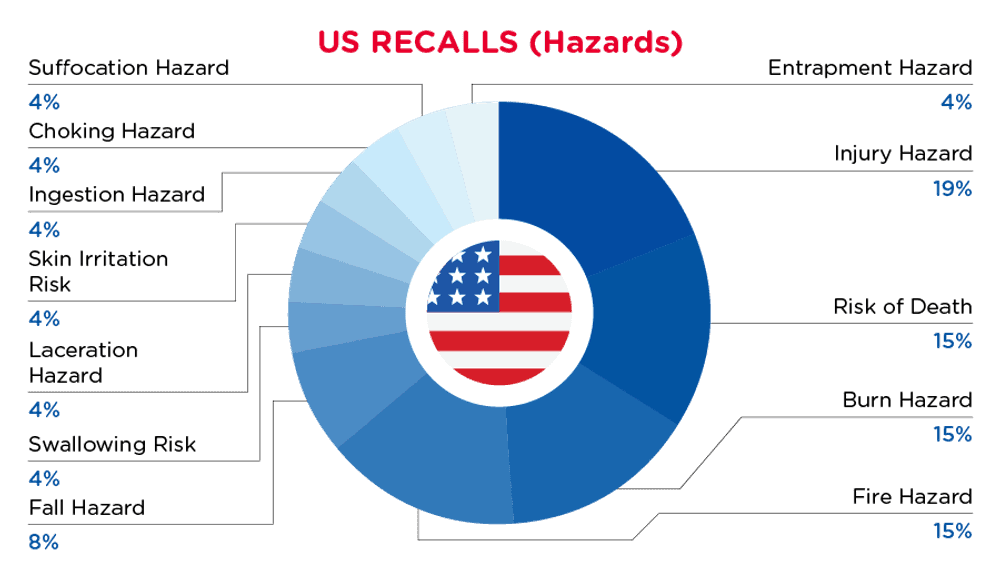
| Hazards | Frequency |
| Injury Hazard | 4 |
| Risk of Death | 3 |
| Burn Hazard | 3 |
| Fire Hazard | 3 |
| Fall Hazard | 2 |
| Swallowing Risk | 1 |
| Laceration Hazard | 1 |
| Skin Irritation Risk | 1 |
| Ingestion Hazard | 1 |
| Choking Hazard | 1 |
| Suffocation Hazard | 1 |
| Entrapment Hazard | 1 |

| Product Categories | Frequency |
| Toys and Childcare Products | 8 |
| Electrical Appliances | 3 |
| Home Electrical Appliances | 3 |
| Household Items | 2 |
| Sporting Goods / Equipment | 2 |
| Chemicals | 1 |
| Fabric / Textile / Garment / Home Textile | 1 |
| Machinery | 1 |
| Outdoor Living Items | 1 |
For a complete list click here
In Canada, when hazards are identified in consumer products, they will be recalled and published in the Recalls and Safety Alerts Database on the Health Canada website, which is updated daily. The Canada recalls from 01 August 2024 to 31 August 2024 are summarized below:
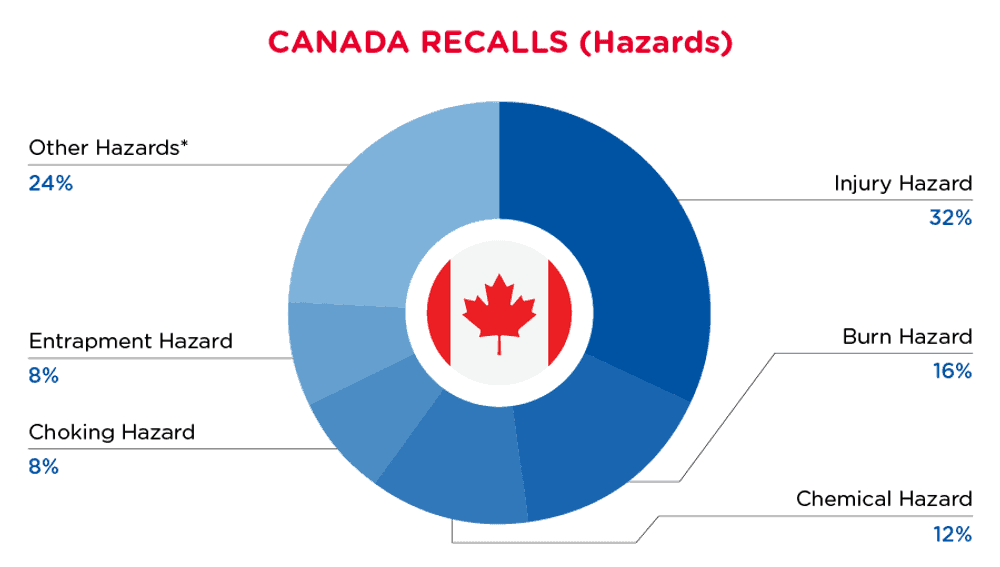
| Hazards | Frequency |
| Injury Hazard | 8 |
| Burn Hazard | 4 |
| Chemical Hazard | 3 |
| Choking Hazard | 2 |
| Entrapment Hazard | 2 |
| Other Hazards* | 6 |
*Other Hazards include Damage to Sight, Damage to Skin, Fire Hazard, Laceration Hazard, Risk of Death and Suffocation Hazard with a frequency of less than 2.

| Product Categories | Frequency |
| Toys and Childcare Products | 6 |
| Fabric / Textile / Garment / Home Textile | 4 |
| Bodycare / Cosmetics | 2 |
| Car Accessories | 2 |
| Chemicals | 2 |
| Electrical Appliances | 1 |
| Protective Equipment | 1 |
| Home Electrical Appliances | 1 |
| Machinery | 1 |
For a complete list click here
Europe News
The European Commission has added a new entry of 79 in Annex XVII to Regulation (EC) No 1907/2006 which restricts the use of PFHxA, its salts and PFHxA-related substances. These sub-groups of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances will be banned in consumer textiles, food packaging, cosmetics, etc. Manufacturers with related products shall pay attention to ensure product compliance.
On 19 September 2024, the European Commission released the restriction related to the use of Perfluorohexanoic acid (PFHxA), its salts and PFHxA-related substances, as an important step forward in reducing per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) emissions. PFHxA is often used as a substitution for perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA), another already banned PFAS. This was added as entry 79 in Annex XVII to Regulation (EC) No 1907/2006 which focuses on ensuring protection of human health and the environment by promoting responsible use of chemicals, encouraging the substitution of hazardous substances with safer alternatives, and increasing transparency about the properties and uses of chemicals.
It will take effect after transitional periods of between 18 months and 5 years, depending on the use, allowing time for replacement by safer alternatives. Manufacturers with related products shall pay attention to ensure product compliance.
Having a linear or branched perfluoro pentyl group with the formula C5F11- directly attached to another carbon atom as one of the structural elements; or
Having a linear or branched perfluorohexyl group with the formula C6F13-.
The following substances are excluded from this designation:
C6F14.
C6F13-C(=O)OH, C6F13-C(=O)O-X′ or C6F13-CF2-X′ (where X′ = any group, including salts)
Any substance having a perfluoroalkyl group C6F13- directly attached to an oxygen atom at one of the non-terminal carbon atoms.
1. Reference for PFHxA-related substances
PFHxA-related substances are substances that, based on their molecular structure, are considered to have the potential to degrade or be transformed to PFHxA. A non-exhaustive list of substances belonging to the scope of the restriction proposal is available on the website of the European Chemicals Agency.
2. Phase-Out Schedule
| Regulation | Product/Scope | Requirement | Effective Date |
| EU REACH Regulation (EC) No 1907/2006 Annex XVII Entry 79 | - Textiles, leather, furs and hides in clothing and related accessories for the general public. - Footwear for the general public. - Paper and cardboard used as food contact materials. - Cosmetics. - Mixtures for the general public. | PFHxA and its salts: ≤ 25 ppb PFHxA related substances ≤ 1000 ppb | 10 October 2026 |
| Textiles, leather, furs and hides, other than in clothing and related accessories referred to 1), for the general public. | 10 October 2027 | ||
| Firefighting foams/ concentrates for training and for testing, or for public fire services, except where those services intervene at industrial fires at establishments covered by Directive 2012/18/EU (relating to the control of major-accident hazards involving dangerous substances) | 10 April 2026 | ||
| Firefighting foams/ concentrates for civil aviation (including in civilian airports) | 10 October 2029 |
The restriction shall not apply to the following:
Personal protective equipment within the scope of Regulation (EU) 2016/425 (outlines requirements for the design, manufacture, and marketing of personal protective equipment (PPE)).
Medical devices within the scope of Regulation (EU) 2017/745 (medical device specific regulation).
In Vitro diagnostic medical devices within the scope of Regulation (EU) 2017/746 (sets standards for in vitro diagnostic medical devices).
Substances having a perfluoroalkyl group C6F13- directly attached to a sulphur atom that are prohibited in Annex I to Regulation (EU) 2019/1021 (POP) (protects human health and the environment by restricting or banning the production and use of persistent organic pollutants (POPs)).
It will be important for manufacturers to focus on the effective dates for their representative products to ensure compliance.
The European Directorate for the Quality of Medicines & Healthcare recently updated the technical guide for food contact metals and alloys to 2024 2nd -edition. This guide can be applied immediately.
On 1 August 2024, the European Directorate for the Quality of Medicines & Healthcare (EDQM), updated the technical guide for food contact metals and alloys. Compared with the previous 1st edition, the revised 2nd edition represents a significant update. The main changes are as follows:
1. Scope revised:
Removed the description of “metals and alloys used in food contact materials and articles that are covered by an organic surface coating that has been demonstrated to restrict release of metal ions to less than the applicable specific release limit” from the unapplicable scope.
That means all coated metal and alloy should follow the requirements in this guide.
Specific release limit (SRL) updated:
Table 1- SRLs for metals and alloy components
| Item | Element | SRL in 2nd guide (mg/kg food) | SRL in 1st guide (mg/kg food) |
| 1 | Aluminum (Al) | 5 | 5 |
| 2 | Antimony (Sb) | 0.04 | 0.04 |
| 3 | Chromium (Cr) | --- | 0.250 |
| 4 | Chromium (Cr) (III) | 1 | --- |
| 5 | Cobalt (Co) | 0.02 | 0.02 |
| 6 | Copper (Cu) | 4 | 4 |
| 7 | Iron (Fe) | 40 | 40 |
| 8 | Magnesium (Mg) | ---b | --- |
| 9 | Manganese (Mn) | 0.55 | 1.8 |
| 10 | Molybdenum (Mo) | 0.12 | 0.12 |
| 11 | Nickel (Ni) | 0.14 | 0.14 |
| 12 | Silver (Ag) | 0.08 | 0.08 |
| 13 | Tin (Sn) | 100a | 100 |
| 14 | Titanium (Ti) | ---b | --- |
| 15 | Vanadium (V) | 0.01 | 0.01 |
| 16 | Zinc (Zn) | 5 | 5 |
| 17 | Zirconium (Zr) | 2 | --- |
a Except in the field of application under Commission Regulation (EU) 2023/915 on maximum levels for certain contaminants in food.
b The generic SRL of 60 mg/kg food is not applicable.
Table 2- SRLs for metals as contaminants and impurities
| Item | Element | SRL in 2nd guide (mg/kg food) | SRL in 1st guide (mg/kg food) |
| 1 | Arsenic (As) | 0.002 | 0.002 |
| 2 | Barium (Ba) | 1.2 | 1.2 |
| 3 | Beryllium (Be) | 0.01 | 0.01 |
| 4 | Cadmium (Cd) | 0.005 | 0.005 |
| 5 | Lead (Pb) | 0.010 | 0.010 |
| 6 | Lithium (Li) | 0.048 | 0.048 |
| 7 | Mercury (Hg) | 0.003 | 0.003 |
| 8 | Thallium (Tl) | 0.001 | 0.0001 |
3. Updated declaration of compliance (DoC):
The 2024 2nd edition removed the previous Chapter 4 of DoC part.
The DoC of products regulated in this guide should follow the requirements in Section 8.2 of Resolution CM/Res (2020)9 on the safety and quality of materials and articles for contact with food.
4. Optimized test conditions:
Added instruction for material/article in contact with dry food:
If an article is intended for contact with only a specific dry food, it should be tested with that food.
Updated test conditions for different types of migration:
Removed specific test conditions for fillable and non-fillable articles; follow actual conditions of use or apply the European Commission's Joint Research Centre (JRC) Guide on testing conditions for kitchenware articles.
Changed the test method for hot beverage appliances:
Replaces DIN 10531 with EN 16889:2016.
Applied a reduction factor of 5 to the SR of silver for silver or silver-plated cutlery in the following products:
Type of class FSI/CAH1* in JRC guide, testing with citric acid as a simulant.
Articles regulated by EN ISO 8442-2, Materials and articles in contact with foodstuffs — Cutlery and table holloware.
Articles labeled not for daily use or not suitable for cooking and food preparation.
This revised technical guide can be used for immediate reference.
In June 2024, the European Committee proposed the draft regulation to update the limitation of use of BPA, as well as to introduce the harmonized classification of bisphenols and bisphenol derivatives potentially used in food contact materials. This regulation is intended to go into effect in November 2024.
The European Union (EU) drafted a regulation addressing updates particular to Bisphenol A (BPA) and other bisphenols and bisphenol derivatives in certain food contact materials (FCM) and articles in June 2024. This draft regulation is a specific measure within the meaning of Article 5 of Regulation (EC) No 1935/2004, relating to materials and articles intended to come into contact with foodstuffs.
The main points in the draft EU regulation are:
1. Definitions:
Table 1
| bisphenol | a substance consisting of two hydroxyphenyl functional groups linked by one bridging atom, in accordance with structure A: - Including the salt form of a bisphenol. - Additional groups may be attached to the bridging atom (structure A) |
| bisphenol derivative | A substance indicated by the following structure B: - Not including the salt form of a bisphenol. - R1 to R10 refers to any substituent. At least one of the substituents is not a hydrogen atom (H), e.g., BADGE (CAS 1675-54-3) - X refers to any bridging group separating the two phenyl rings by one single atom, but the atom can have any substituent(s). (structure B) |
| Hazardous bisphenol or hazardous bisphenol derivative | A bisphenol or a bisphenol derivative listed in Part 3 of Annex VI to Regulation (EC) No 1272/2008 on classification, labelling and packaging of substances and mixtures, due to its harmonized classification as category 1A or 1B ‘mutagenic’, ‘carcinogenic’, ‘toxic to reproduction’ or category 1 ‘endocrine disrupting’ for human health’ |
2. Current application of BPA
3. Prohibition of BPA:
Table 2
| Item | Draft BPA regulation | EU 10/2011 |
| Tolerable Daily Intake (TDI) | TDI in 2023: 0.2 ng/kg | TDI in 2015: 4 μg/kg |
| Requirement | BPA and its salts prohibited Specific migration limits (SML) for the derogation: ND (DL: 1μg/kg) | 0.05 mg/kg |
| Restrictions and Specifications | By way of derogation from BPA prohibition, BPA and its salts may be used in the manufacture of: epoxy resins to be applied on self-supporting food contact materials or articles with a capacity greater than 1000 liters. a monomer or starting substance in the manufacture of polysulfone filtration membrane assemblies. | Not to be used for the manufacture of polycarbonate infant feeding bottles. Not to be used for the manufacture of polycarbonate drinking cups or bottles which, due to their spill proof characteristics, are intended for infants and young children. |
4. Restriction of other bisphenols and bisphenol derivatives:
FCM manufactured using another bisphenol or bisphenol derivative shall not contain any residual BPA.
Without evaluation and authorization, hazardous bisphenols other than BPA or hazardous bisphenol derivatives are prohibited.
5. Verification of compliance:
BPA residual: extraction method.
BPA migration: the rules and parameters are the same as EU 10/2011 on plastic materials and articles intended to come into contact with food.
Analytical methods uniformly applied throughout the Union are required to be developed.
6. Declaration of compliance:
Accompany the FCM at all stages of placing on the market, except during the retail stage.
Include an indication whether BPA or other relevant bisphenols or bisphenol derivatives have been used.
7. Transition period:
Table 3
| Product types | Transition period |
| General articles | 18 months |
| Packaging with varnishes and coatings manufactured with BPA, specifically used to preserve fruit, vegetables and processed fish products | 36 months |
| Metal packaging in which external/ internal surfaces have had BPA varnishes and coatings applied | 36 months |
| Single-use final FCM (including metal packaging) | Should be filled with food and sealed within 12 months from the end of the respective transitional periods, until exhaustion of stocks. |
| Repeat-use components in professional food production equipment, such as confectionary molds, seals, pumps, flanges, gauges and sight glasses | 36 months |
| Repeat-use final food contact articles that have been first placed on the market by their manufacturers | In order to avoid large stocks, sales can continue for a maximum period of one year. |
| Repeat-use final food contact articles used as professional food production equipment | Continue to use until falling into disuse. |
8. Relationship with other regulations:
1. Repeal Regulation (EU) 2018/213 on the use of bisphenol A in varnishes and coatings intended to come into contact with food
The measures provided for in this Regulation supersede the measures laid down in Regulation (EU) 2018/213. It is therefore appropriate to repeal (EU) 2018/213.
2. Amending Regulation (EU) No 10/2011
By way of derogation from Article 5, BPA and other hazardous bisphenols or hazardous bisphenol derivatives added.
In Table 1 of Annex I, the entries concerning substance No. 151 (BPA) and substance No. 154 (BPS) are deleted.
This draft regulation is intended to go into effect in November 2024.
The European Chemical Agency has announced a consultation phase for the potential inclusion of six chemicals as SVHC. Should these listings be approved, the number of substances recognized as SVHC on the candidate list will be updated to 247 entries.
On 30 August 2024, the European Chemical Agency (ECHA) launched a 45-days public consultation on six new potential Substances of Very High Concern (SVHC), as shown in the table below.
If this is approved, the number of SVHCs on the Candidate List will be updated from 241 entries to 247 entries.
A decision will be made regarding the inclusion of the below substances in the ECHA Candidate List of SVHC after the conclusion of the 45-day consultation period.
| Name of Substance(s) | EC Number | CAS Number | Reason for Proposing |
| 6-[(C10-C13)-alkyl-(branched, unsaturated)-2,5-dioxopyrrolidin-1-yl]hexanoic acid | 701-118-1 | 2156592-54-8 | Toxic for reproduction (Article 57c) |
| O,O,O-triphenyl phosphorothioate | 209-909-9 | 597-82-0 | PBT (Article 57d) |
| Octamethyltrisiloxane | 203-497-4 | 107-51-7 | vPvB (Article 57e) |
| Perfluamine | 206-420-2 | 338-83-0 | vPvB (Article 57e) |
| Reaction mass of: triphenylthiophosphate and tertiary butylated phenyl derivatives | 421-820-9 | 192268-65-8 | PBT (Article 57d) |
| Tris(4-nonylphenyl, branched and linear) phosphite | / | / | Endocrine disrupting properties (Article 57(f) – environment) |
The German Federal Institute for Risk Assessment (BfR) recently updated recommendations for five types of food contact materials. A manufacturer of silicone/paper/ temperature-resistant coatings should be aware that test methods or requirements has been revised. These updated documents can be applied immediately.
On 1 August 2024, the German Federal Institute for Risk Assessment (BfR) issued five updated recommendations relative to food contact materials. Following are the updated recommendations and affected food contact materials:
| Reference # | |
| XV | Silicones |
| XXXVI | Paper and Board for Food Contact |
| XXXVI/1 | Cooking Papers, Hot Filter Papers and Filter Layers |
| XXXVI/2 | Paper and Paperboard for Baking Purposes |
| LI | Temperature Resistant Polymer Coating Systems for Frying, Cooking and Baking Utensils |
The main changes of the requirements and test methods are:
1. For XV Silicones:
Deleted the requirement for extractable components (Section III, 5) not exceeding 0.5%.
Updated the test method for Volatile Organic Matter (VOM):
Table 1
| Item | Updated version on 1 August 2024 | Previous version |
| VOM | After conditioning, specimen is tested at 200℃ for 4 hours. | After conditioning, specimen is tested at 200℃ for 4 hours. |
| VOM | Articles that cannot withstand above testing conditions, can apply alternative conditions in Table 3 of Annex V in Regulation (EU) 10/2011. | After conditioning, specimen is tested at 200℃ for 4 hours. |
2. For XXXVI Paper and Board for Food Contact:
Updated the requirement for Phthalates for recycled paper:
Table 2
| Specified Phthalate | Updated version on 1 August 2024 | Previous version |
| DEHP | 0.6 mg/kg | 1.5 mg/kg |
| DBP | 0.12 mg/kg | 0.3 mg/kg |
| DIBP | 0.15 mg/kg | 0.3mg/kg |
| Sum of (DBPx5 + DIBPx4 + DEHPx1) report as DEHP | 0.6mg/kg | / |
3. For XXXVI/1 Cooking Papers, Hot Filter Papers and Filter Layers and XXXVI/2 Paper and Paperboard for Baking Purposes:
There is no update for requirement or test method.
Compared with previous version, species of additives have been included.
4. For LI Temperature Resistant Polymer Coating Systems for Frying, Cooking and Baking Utensils:
Added requirement of 10mg/dm2 for overall migration of 3rd migration test. Test conditions as follows:
95% ethanol, 60 ℃ for 6 hours.
Isooctane, 60 ℃ for 4 hours.
Updated test conditions for specific migration:
Remove test conditions in previous version.
Apply test conditions in European Commission's Joint Research Centre (JRC) Guide for food preparation utensils under classes FPU/H2, FPU/H3, and a modified time for FPU/H4 to 4 hours.
Apply modified polyphenylene oxide (MPPO) as simulant for article contact with dry food; test condition is 175 °C for 2 hours (DIN EN 14338).
Apply the current version of European Directorate for the Quality of Medicines & HealthCare (EQDM) Technical Guideline for Metals and Alloys for element migration testing.
Note: These updated documents can be applied immediately.
In Europe, when hazards are identified in non-food consumer products, the products will be recalled and published in the Safety Gate system, which is updated weekly. The European recalls from 01 August 2024 to 31 August 2024 are summarized below:
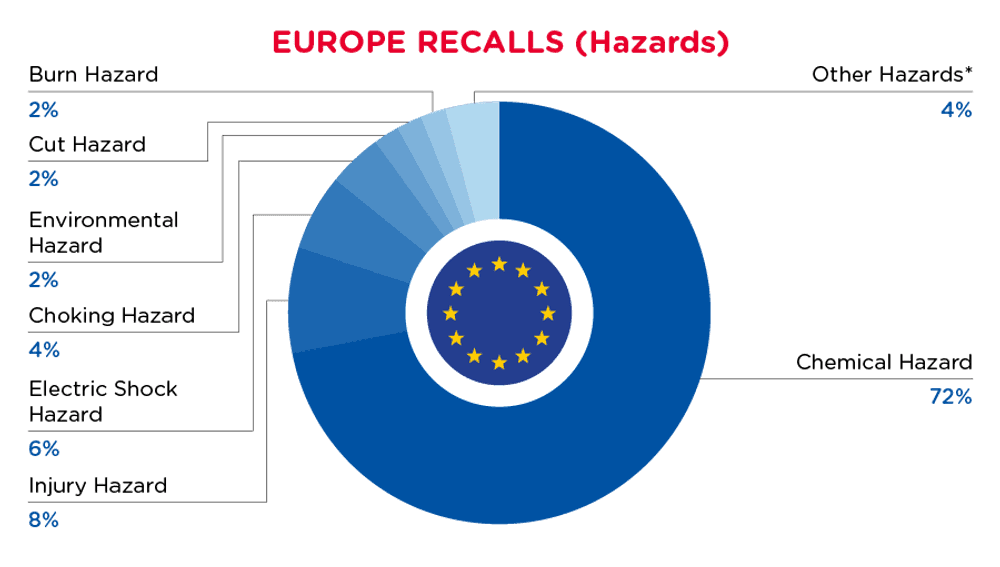
| Hazards | Frequency |
| Chemical Hazard | 398 |
| Injury Hazard | 42 |
| Electric Shock Hazard | 31 |
| Choking Hazard | 21 |
| Environmental Hazard | 13 |
| Cut Hazard | 12 |
| Burn Hazard | 12 |
| Other Hazards* | 24 |
*Other Hazards include Strangulation Hazard, Damage to Sight, Drowning Hazard, Fire Hazard, Suffocation Hazard, Damage to Hearing, Microbiological Hazard and Entrapment Hazard with a frequency of less than 7.

| Product Categories | Frequency |
| Bodycare / Cosmetics | 336 |
| Toys and Childcare Products | 50 |
| Electrical Appliances | 34 |
| Chemicals | 33 |
| Machinery | 22 |
| Fabric / Textile / Garment / Home Textile | 13 |
| Other Categories* | 35 |
*Other Categories include Home Electrical Appliances, Outdoor Living Items, Protective Equipment, Sporting Goods / Equipment, Jewelry, Computer / Audio / Video / Other Electronics & Accessories, Food Contact Material, Tools and Hardware, Furniture and Footwear with a frequency of less than 8.

| Notifying Country | Frequency |
| Italy | 294 |
| Hungary | 55 |
| Czechia | 38 |
| Denmark | 20 |
| Sweden | 15 |
| France | 14 |
| Finland | 14 |
| Lithuania | 13 |
| Poland | 13 |
| Austria | 10 |
| Other Countries* | 37 |
*Other Countries include Germany, Slovakia, Romania, Cyprus, Norway, Ireland, The Netherlands, Bulgaria, Belgium and Latvia with a frequency of less than 10.
For a complete list click here
China News
In China, when hazards are identified in consumer products, they will be recalled and published in the SAMR Defective Product Administrative Centre, which is updated daily. The China recalls from 01 August 2024 to 31 August 2024are summarized below:
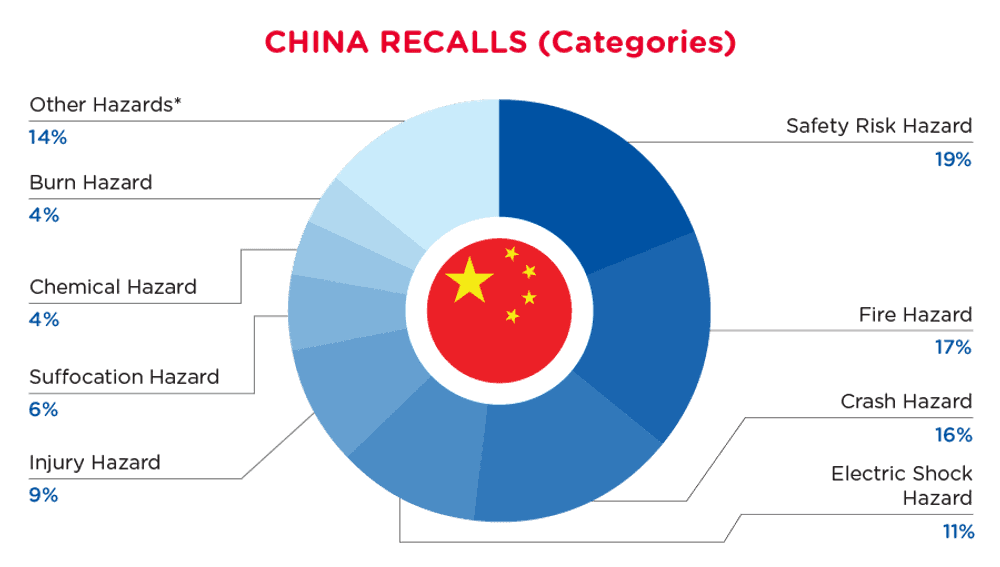
| Hazards | Frequency |
| Safety Risk Hazard | 25 |
| Fire Hazard | 23 |
| Crash Hazard | 21 |
| Electric Shock Hazard | 15 |
| Injury Hazard | 12 |
| Suffocation Hazard | 8 |
| Chemical Hazard | 6 |
| Burn Hazard | 5 |
| Other Hazards* | 19 |
*Other Hazards include Explosion Hazard, Swallowing Risk, Fall Hazard, Damage to Sight, Damage to Hearing, Puncture Hazard, Entanglement Hazard, Health Risk Hazard and Laceration Hazard with a frequency of less than 4.

| Product Categories | Frequency |
| Sporting Goods / Equipment | 44 |
| Toys and Childcare Products | 21 |
| Home Electrical Appliances | 6 |
| Electrical Appliances | 5 |
| Stationery | 3 |
| Other Categories* | 7 |
*Other Categories include Food Contact Material, Computer / Audio / Video / Other Electronics & Accessories, Household Items, Fabric / Textile / Garment / Home Textile, Protective Equipment and Tools and Hardware with a frequency of less than 3.
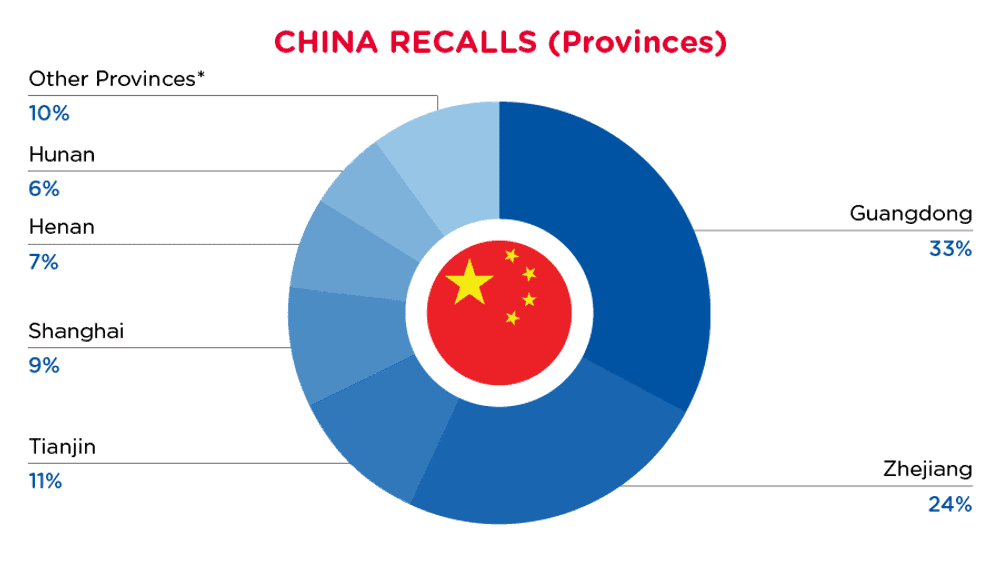
| Provinces | Frequency |
| Guangdong | 28 |
| Zhejiang | 21 |
| Tianjin | 9 |
| Shanghai | 8 |
| Henan | 6 |
| Hunan | 5 |
| Other Provinces* | 9 |
*Other Provinces include Inner Mongolia, Fujian, Jiangsu, Sichuan, Liaoning and Shanxi with a frequency of less than 2.
For a complete list click here
Australia/New Zealand News
In Australia, when hazards are identified in consumer products, they will be recalled and published in the Recalls and Safety Alerts Database on the Australian Competition & Consumer Commission website, which is updated daily. The Australia recalls from 01 August 2024 to 31 August 2024are summarized below:
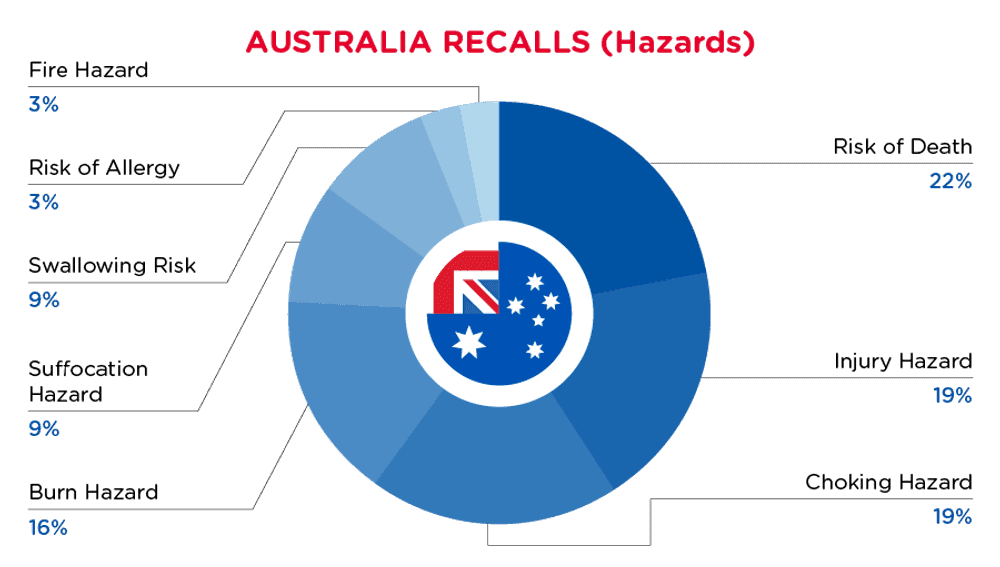
| Hazards | Frequency |
| Risk of Death | 7 |
| Injury Hazard | 6 |
| Choking Hazard | 6 |
| Burn Hazard | 5 |
| Suffocation Hazard | 3 |
| Swallowing Risk | 3 |
| Risk of Allergy | 1 |
| Fire Hazard | 1 |

| Product Categories | Frequency |
| Fabric / Textile / Garment / Home Textile | 5 |
| Toys and Childcare Products | 2 |
| Electrical Appliances | 2 |
| Sporting Goods / Equipment | 2 |
| Bodycare / Cosmetics | 1 |
| Household Items | 1 |
For a complete list click here
USA Federal News
On 5 September 2024, the United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) issued a Direct Final Rule that will delay the beginning of the submission period for PFAS data until 11 July 2025. There are no other changes to the reporting and recordkeeping requirements in the existing rule under TSCA (40 CFR Part 705).
The United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) issued a Direct Final Rule on 5 September 2024 that will delay the data submission start date for per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) data reporting and recordkeeping required under the Toxic Substances Control ACT (TSCA). The delay moves the start date from 12 November 2024 to 11 July 2025. No other changes to the reporting and recordkeeping requirements in the existing rule under TSCA (40 CFR Part 705) were implemented.
Background on the TSCA Section 8(a)(7) reporting and recordkeeping requirements for PFAS
As promulgated in October 2023, the regulation requires manufacturers (including importers) of PFAS in any year between 2011-2022 to report certain data to the EPA related to exposure and environmental and health effects.
Citing general budgetary issues and resource constraints, the EPA's contractors reduced their effort on the TSCA information technology software and related portfolio by more than 50 percent, which had significant, immediate implications for the EPA's ability to make progress on many of its information technology / information management (IT/IM) projects.
To ensure functioning reporting capabilities, the EPA must extend the development project timeline. Therefore, the beginning of the data submission period has changed from 12 November 2024 to 11 July 2025. Most reporters of this data will be required to complete all reporting by 22 January 2026. Those small businesses reporting data solely on importing PFAS contained in articles will have until 11 July 2026 to submit reports.
Impact to Regulated Entities
Strategic initiatives surrounding PFAS under the TSCA regulation have great impact on manufacturers and importers. Regulated entities need to consider not only whether their own operations involve products that contain PFAS, but also whether the products within their supply chain might contain PFAS. The delayed start of the reporting period allows related entities to be well prepared on this robust reporting obligation.
It should be noted that, even though budgetary and resource issues resulted in a delay of the data collection requirement, the window to perform such a large data collection and compile the mandatory reports is quickly closing. It shows the EPA’s steadfast dedication to proceeding with this reporting, as initially proposed.
Subscribe to our Regulatory Updates
Unsubscribe at any time. Read our privacy policy.