Table of Contents
Acceptable Quality Limit (AQL)
How Do I Determine the Correct Sample Size and Acceptance Number?
AQL Sampling Simulator
Table A
Table B
Ready to Simulate Your AQL Sampling
More Resources
Need more information?
By contacting QIMA you agree to our privacy policy and terms and conditions.
Acceptable Quality Limit (AQL)
The Acceptance Quality Limit (AQL) is used in product inspections to determine the maximum acceptable number of defective items in a sample batch. If the number of defective items is higher than the maximum acceptable limit, the batch is rejected. AQL is typically set differently for minor, major, and critical defects. Since critical defects are unacceptable, AQL for critical defects is commonly 0.
In sampling inspections, QIMA inspectors follow the ISO 2859 standard, which forms the basis for the Acceptable Quality Limit (AQL) methodology. The standard provides tables to determine sample sizes and defect thresholds, ensuring precise and reliable quality assessments.
Our inspectors use pre-defined sampling plans to perform a detailed analysis of production samples, verifying whether they meet the AQL. Our transparent, AQL-based approach to sampling inspections helps you make informed decisions on whether to accept or reject an entire batch.
AQL Benefits
Inspecting a sample of products from a batch in a consistent and systematic way, instead of testing every single item, provides significant benefits:
Saves time and reduces costs while still maintaining acceptable quality standards.
Helps balance the risk of accepting defective products against the cost and effort of inspection.
Allows different AQL levels for different products or defect types, supporting varying quality requirements.
Provides clear criteria for accepting or rejecting a batch, simplifying the decision-making process.
How do I Determine the Correct Sample Size and Acceptance Number?
Our experts will guide you in selecting the inspection level and AQL values that best fit your requirements. Use our AQL sampling calculation tool to simulate product inspections and gain a better understanding of how the process works.
For example, if you need to inspect 4,000 face masks using a normal inspection (Level II with an AQL of 2.5), simply enter the relevant data into the designated fields in the AQL calculator below:
Quantity: 4000
Inspection level: General Inspection II
AQL: 2.5
AQL Sampling Simulator
Table A
Find the respective Lot Size (quantity) and general inspection level: Code letter L Note: The AQL tables below are based on the ANSI/ASQ Standard Z1.4 – 2008
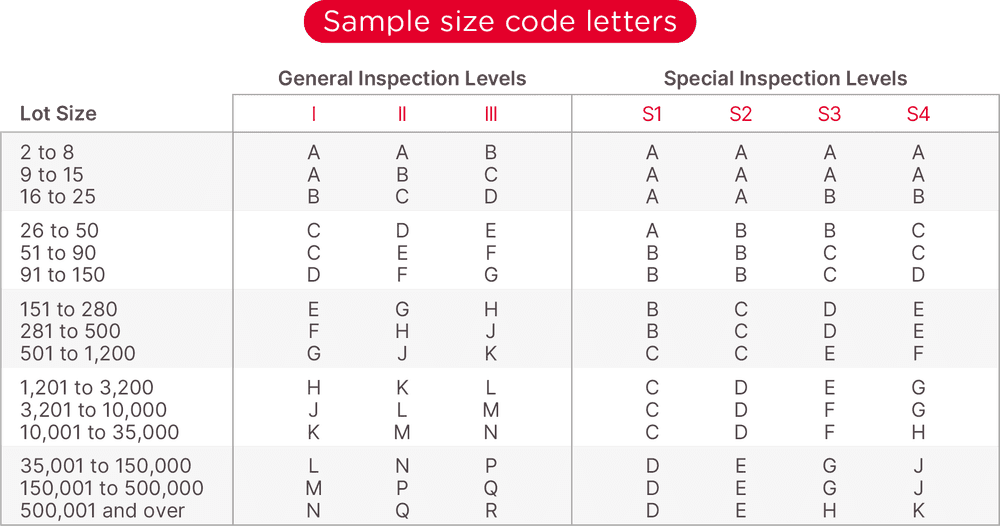
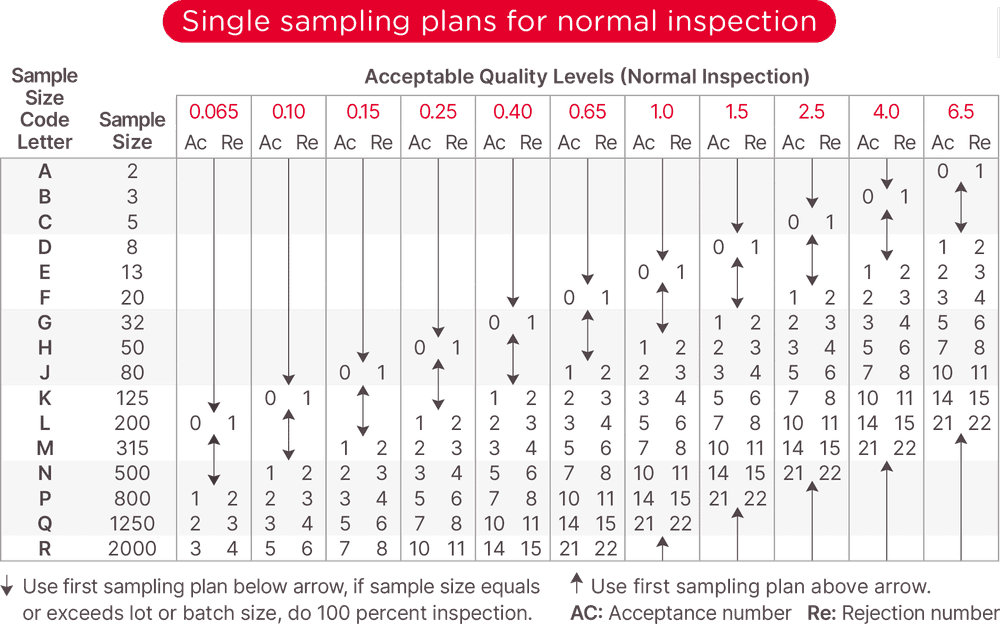
Table B
Locate Row L (the required sample size of 200) In compliance with AQL 2.5, no more than 10 units from a sample size of 200 may fail the inspection.
Simulate Your AQL Sampling
Go ahead and simulate your next sampling inspection:
Enter your shipment lot quantity
Select General/Special inspection level
Select AQL for all defects (critical, major, minor)
Refer to Tables A and B above to see the impact on inspected quantities and accepted defect limits
