News Article
QIMA 2025 Q1 Barometer - Global Supply Chains Prepare for Uncertainty as New Trade Wars Loom
Global Supply Chains Prepare for Uncertainty as New Trade Wars Loom
Global supply chains demonstrated resilience in 2024 despite mounting disruptions, with stable demand in Western markets contributing to the recovery of trade after the downturn in 2023. Now, the sourcing landscape is braced for new uncertainties, as new tariffs and protectionism loom in the coming year. This barometer report, informed by QIMA’s aggregated data on product inspections and factory audits, provides a retrospective of 2024 in consumer products sourcing, and expectations for 2025, including the potential impact of the escalating US/China trade war on major sourcing regions.
2024 Marks a Year of Steady Growth for Global Procurement
Despite numerous disruptions that ranged from geopolitics to extreme weather, 2024 proved to be a strong year for sourcing. Global procurement volumes showed a consistent upward trend, with QIMA data showing demand for supply chain inspections and audits expanding +24% year-over-year (YoY) among European buyers, and +15% YoY among US-based brands and retailers. Inspection and audit demand was even more vigorous among businesses in emerging markets, particularly in Latin and South America (+60% YoY), where imports were boosted by domestic demand as well as US nearshoring initiatives.
Western Demand for Made-in-China Rose in 2024, Driven by Supply Chain Disruptions and Anticipation of Trump Tariffs
QIMA data suggests that China remained a key sourcing partner of global supply chains in 2024, with robust growth in inspection and audit demand from buyers worldwide (+29% YoY), across all major consumer goods categories.
Demand for China inspections and audits from EU-based buyers rose by +22% YoY in 2024, with American businesses only slightly behind at +17% YoY. This suggests that despite the ongoing supply chain shifts, western brands and retailers still regard China as a reliable fallback when manufacturing capacity runs short in other supplier hubs across Asia and near-shoring regions.
The anticipation of new US tariffs on Chinese goods may have also driven the increased demand for China procurement in 2024. Some Western brands and retailers, in particular, have reported stocking up on made-in-China goods, building up inventory buffers to minimize business disruptions during any potential re-routing of sourcing; other brands and retailers, meanwhile, adopt a wait-and-see approach, recognizing that replacing China as a source won’t be possible overnight. The next stage of the US/China trade war – which is highly likely, given the current geopolitical climate – is expected to be a major factor in how global supply chains approach China sourcing in 2025.
Mexico Attracts Scrutiny as a Potential Country-of-Origin Loophole for Chinese Goods
Mexico’s rapidly expanding trade with China, evidenced by a +64% YoY increase in inspection and audit demand in 2024, along with the growth of nearshoring projects, has raised questions as to whether Chinese businesses are increasingly using Mexico as a proxy to bypass existing US tariffs on goods made in China.
QIMA data for 2024 shows that US demand for inspections and audits in Mexico has been growing at a fraction of the pace of Mexican businesses’ demand for China inspections and audits. This suggests that, at least for fast-moving consumer goods, the lion’s share of Mexico’s current sourcing from China is likely intended for its domestic market. And while relocating final product assembly closer to the US market may be attractive for Chinese exporters at the moment, they will have to carefully weigh their options in the light of the potential higher US tariffs against both China and Mexico (as well as revision of the United States-Mexico-Canada trade agreement slated for 2026).
Brands Embrace Limited-Scale Nearshoring to Mitigate Sourcing Risks
After contributing to Mexico’s crowning as the US’s largest trading partner in 2023, US nearshoring in Mexico may now be at risk due to tariff threats from the incoming Trump administration. However, QIMA data indicates that US-based brands and retailers are actively exploring other sourcing partnerships across Latin and South America, including in Guatemala, Peru, Brazil, and the Dominican Republic, where US demand for inspections and audits has grown +20% YoY in 2024. Such diversification of supplier portfolios is likely to make US nearshoring projects less vulnerable to tariff tensions with Mexico.
Overall, aggregated QIMA data on inspection and audit demand also suggests that nearshoring has only been growing slowly in the West. After initially redirecting some sourcing volumes closer to home, both US-based and EU-based buyers now seem to favor diversifying their overseas procurement further, without significantly increasing the share of nearshoring in their sourcing portfolios. This limited incorporation of local sourcing suggests a growing trend towards “multi-shoring” and the use of regional supply hubs as part of brands’ strategies for risk mitigation and enhanced supply chain flexibility.
Fig. N1: Relative share of overseas and respective home regions in procurement for US- and EU-based buyers
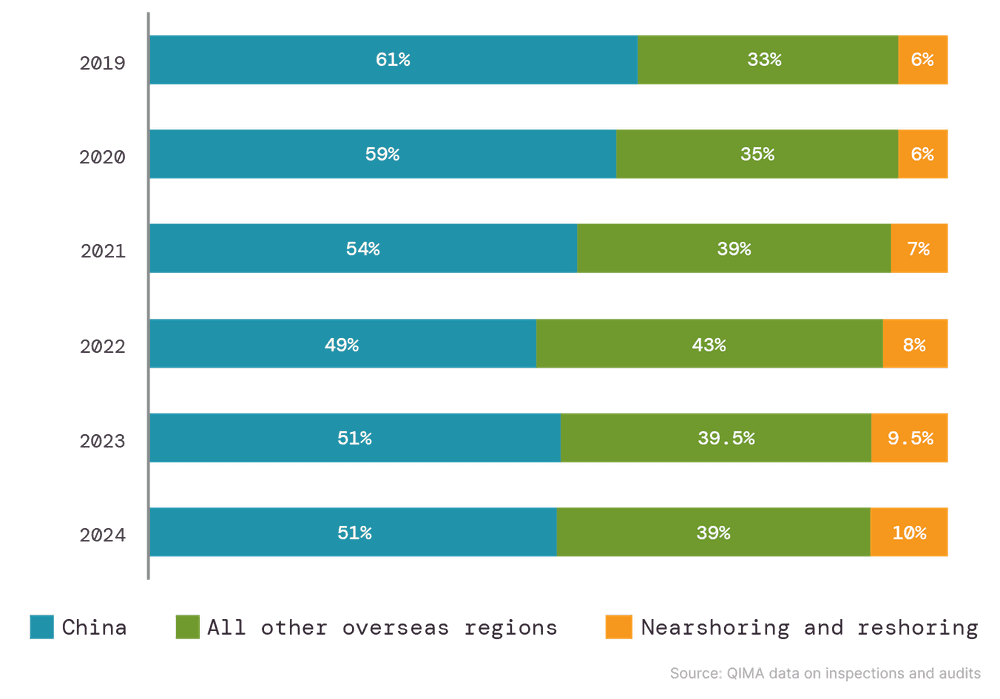
Source: QIMA data on inspections and audits
Supplier Markets Across Asia Wrap Up a Strong Year, Benefiting from the Ongoing Supply Chain Shifts
Supplier hubs in Southeast and South Asia were popular with buyers globally during 2024, and performed strongly despite multiple disruptions.
Vietnam remained one of the key beneficiaries of the ongoing sourcing shifts from China, with QIMA data showing demand for inspections and audits expanding by +30% YoY in 2024 (+26% from US- and EU-based buyers). Looking ahead, the anticipated higher US tariffs on Chinese goods may place Vietnam at an even greater advantage in 2025. However, if viewed as a “middleman country” for Chinese businesses, Vietnam itself may also come under the risk of tariffs.
Other Southeast Asian countries also attracted robust volumes of new business from the West in 2024. QIMA recorded double-digit year-over-year growth of inspection and audit demand in Indonesia (+33% YoY), Thailand (+15% YoY) and the Philippines (+50% YoY). The region is expected to remain resilient in the coming year, with economic growth projected at 4.9% in 2025.
South Asian sourcing hubs continued to play a crucial role in the procurement portfolios of US-based and European buyers. QIMA data shows demand for India inspections and audits expanding +25% year-over-year (including +25% YoY growth among Western buyers). Bangladesh also closed 2024 with double-digit growth, despite a challenging year marked by protests, factory shutdowns and extreme weather, highlighting its importance as a key supplier hub for Western brands. Meanwhile, Pakistan and Sri Lanka also saw an increase in manufacturing orders in 2024 as their economies have continued to stabilize following recent economic crises.
Fig. S1: Top sourcing regions of US- and EU-based buyers (by share)
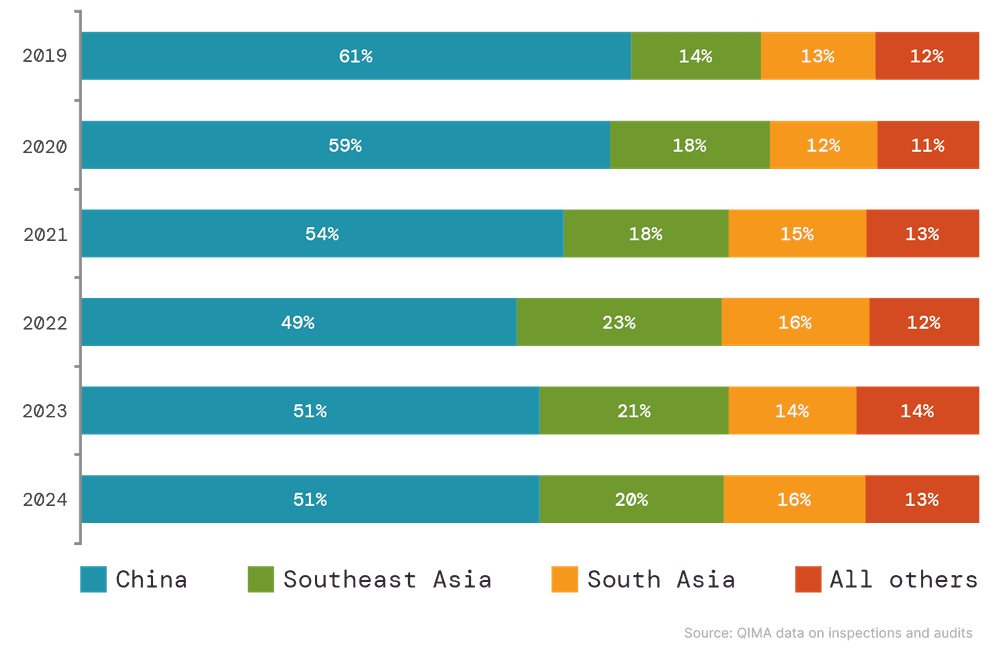
Source: QIMA data on inspections and audits
Fig. S2: Relative shares of South Asian countries in the sourcing portfolio of US- and EU-based buyers (2024)
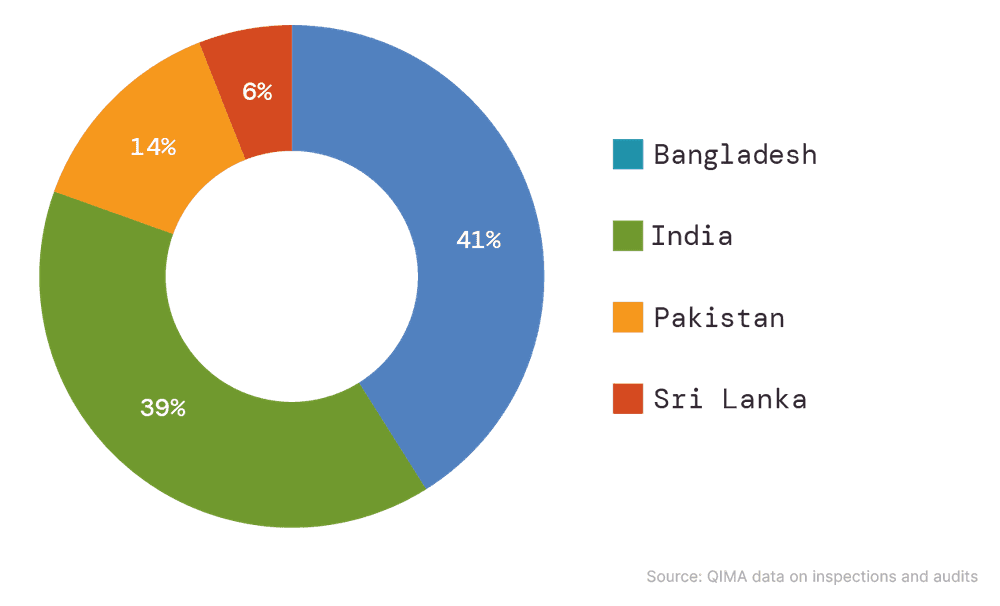
Source: QIMA data on inspections and audits
Despite Legislation Driving Progress on Ethical Compliance, Human Rights Risks Remain an Issue for Supply Chains Globally
The past year saw the continued rollout of legislation mandating human rights and environmental due diligence in supply chains, including the EU Corporate Sustainability Due Diligence Directive adopted in May 2024. QIMA’s factory audit data suggests that this increased legislative pressure is contributing to improved supply chain compliance and sustainability worldwide. Globally, the share of factories ranked “Green” for compliance by QIMA auditors increased to an all-time high of 58%,indicating that over half of factories audited in 2024 met relevant human rights and environmental requirements. At the same time, the ratio of factories assigned a “Red” ranking, which indicates an urgent need for improvement, has remained unchanged from the previous year. This suggests that a certain percentage of facilities tends to resist improvement, a trend previously noted in earlier QIMA barometer reports.
While these findings are a cause for optimism, they do not warrant complacency. Despite the progress being made, significant human rights risks remain in global supply chains. Bangladesh, in particular, made headlines as a human rights hotspot in 2024, with numerous factories shutting down due to worker protests. QIMA audit findings highlight the severity of the problem, with critical violations related to Working Hours and Wages recorded in one-third of Bangladeshi factories inspected in 2024 – a rate notably higher compared to the previous year, as well as the region’s 2024 average of 26%.
Furthermore, ethical risks in supply chains are not confined to Asia and other overseas supplier markets. Emphasizing the growing importance of ethical compliance in the context of nearshoring, QIMA data shows a year-on-year doubling in demand for ethical audits at European factories from EU-based buyers. This trend underscores the increasing emphasis on ethical compliance in sourcing strategies, regardless of geographic location.
Fig. E1: Evolution of factory rankings assigned by ethical audits, 2019-2024 (global averages)
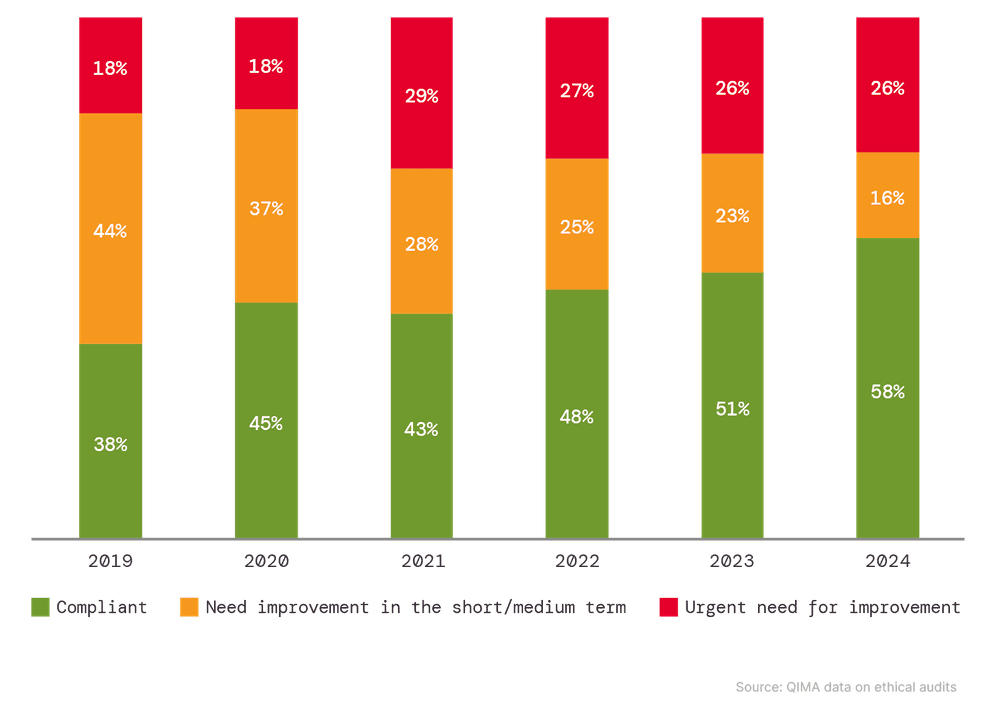
Source: QIMA data on ethical audits
Fig. E2: Incidence of critical violations related to working hours and wages identified during factory audits
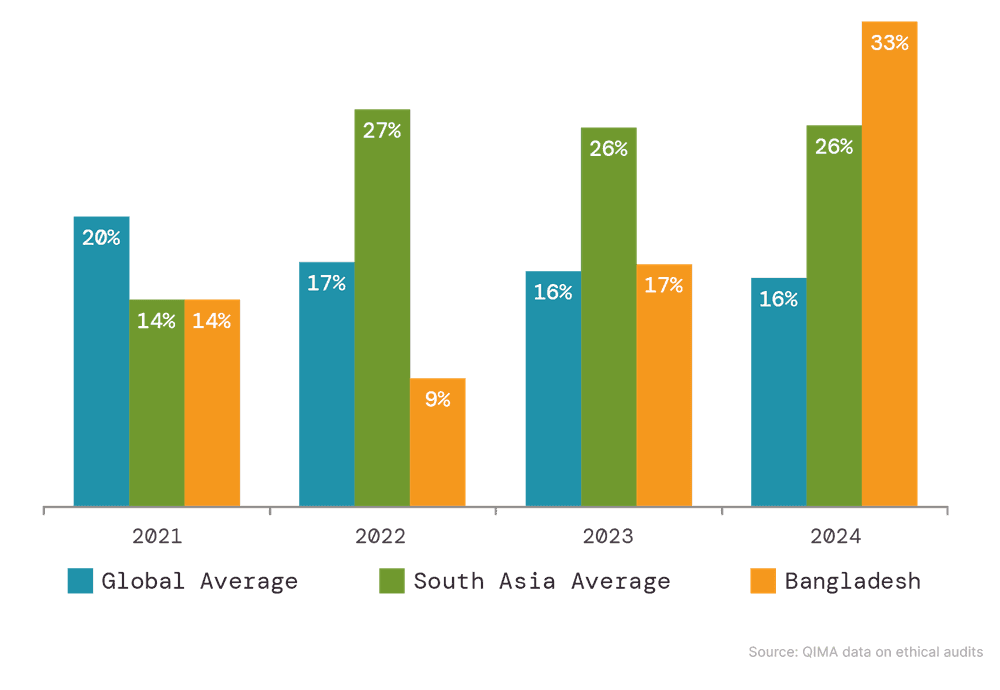
Source: QIMA data on ethical audits